ROBOT WELDING
What is Robot Welding ?
Robot welding is that the use of mechanized programmable tools (robots), which completely automate a welding process by both performing the weld and handling the part. Processes like gas metal arc welding, while often automated, aren’t necessarily like robot welding, since a person’s operator sometimes prepares the materials to be welded. Robot welding is usually used for resistance spot welding and arc welding in high production applications, like the automotive industry.
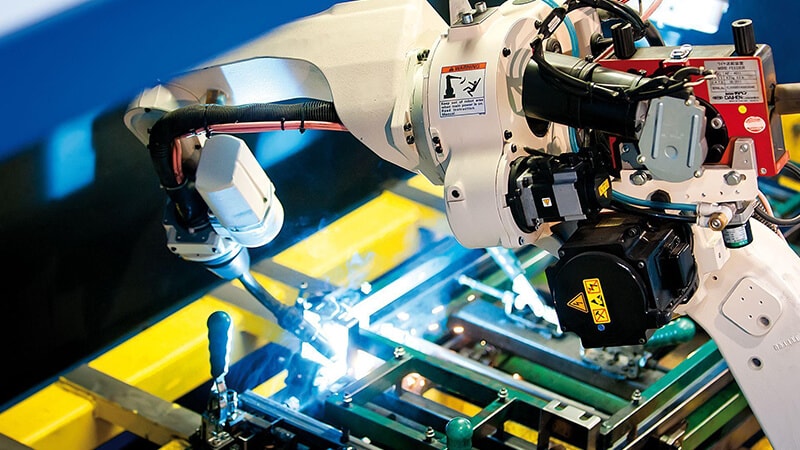
When using robots for any process, the tactic requires amending to accommodate automation. an equivalent is true of welding, which uses several tools not found in its manual equivalent. People don’t need programming the way robotic welders do.
The robot itself has an arm which will move in three dimensions for rectilinear types and thru more planes with articulating versions. A wire feeder sends the filler wire to the robot because it needs it for a welding job. A high-heat torch at the top of the arm melts metal to enable the welding process. Because the temperatures reach thousands of degrees, using robots for this process keeps people safer.
Certified human operators still got to remain on the brink of the robots. These workers should hold certification from the American Welding Society, AWS, which certify not only manual welders but also robotic welding arm operators. The operators program the controller employing a teach pendant. This device sets new programs, moves the arm and changes parameters for the method . to start out the welding, the operator uses the buttons on the operation box.
The tool within the robotic arm heats to melt metal to conjoin the specified pieces. As needed, a wire feeder delivers more metal wire to the arm and torch. When awaiting subsequent parts to weld, the arm moves the torch to the cleaner to wash any metal splatters from the arm, which could solidify in situ without this process.
Because one among the first reasons to possess robotic welders is protecting human workers, these automated systems accompany multiple safety features. Arc shields prevent the high-heat arc from mixing with oxygen. Enclosed areas protect operators from the temperatures and bright light.
Robot Welding Process
1. Arc Welding
One of the foremost common sorts of robotic welding is that the arc process. during this method, an electrical arc generates extreme heat, up to 6,500 degrees Fahrenheit, which melts the metal. Molten metal joins parts together, solidifying into a stable connection after cooling. When a project requires an outsized volume of accurately conjoined metals, arc welding is a perfect application.
2. Resistance Welding
When projects need heat-treating or how to lower costs, robots may use resistance welding. During this process, a current of electricity creates a pool of molten metal because it passes between the 2 metal bases. This molten metal joins the pieces of metal together.
3. Spot Welding
Some materials resist electrical currents, precluding them from other sorts of welding. this example frequently occurs within the automotive industry for piecing together parts of an automobile body. to beat the difficulty , robotic welders use a variation of resistance welding to attach a pair of thin metal sheets during a single spot.
4. Tig Welding
Robot welding applications requiring high levels of precision may require TIG welding. This method also goes by the term gas tungsten arc welding or GTAW. an electrical arc passes between a tungsten electrode and therefore the metal base.
5. Mig Welding
Gas metal arc welding, also referred to as GMAW or MIG, may be a fast and easy method that uses a high level of deposition. A wire moves continuously to the heated tip of the welder, which melts the wire, allowing an outsized amount of molten metal to drip onto the bottom for joining the bottom to a different piece.
6. Laser Welding
When welding projects require accuracy for a high volume of parts, laser welding is that the preferred method of metal joining. Small parts, like jewelry or medical components often use laser welding.
7. Plasma Welding
Plasma welding offers the foremost significant degree of flexibility because the operator can easily change both the speed of gas passing through the nozzle and therefore the temperature.
How Vancouver Automation can help you ?
Material Handling is an essential part of every automation system. Whether moving heavy awkward parts or small intricate precision components, efficient manipulation and control is essential. From the newest motor assembly to the most intricate surgical device, material handling and its flow ensures that components can be turned into assemblies that guarantees an assembly solution will not choke off critical up time or contribute to costly damage to parts or operators. Vancouver Automation through its experience along with its partners to provide technologically leading solutions that ensure the backbone of the custom equipment link together in support and harmony. There are many solutions that are tried and true and new flexible solutions that deal with the complexities in the market today. Material handling solutions range from linear solutions in layout and form too numerous to detail but include our partners: Robert Bosch power and free conveyor, belt driven solutions coupled with flexible feeders, bowls, hoppers with vision, and escapement devices that verify orientation and control throughout the assembly process.





